

溶液對實(shí)現(xiàn)橢偏儀在位監(jiān)測電化學(xué)沉積薄膜主要會帶來兩方面的影響闽晦,第1種是溶液的擾動扳碍,比如在開放的溶液體系,溶液表面的擾動可能會對光產(chǎn)生多種散射機(jī)制仙蛉,從而給測試帶來困難。橢偏儀在位監(jiān)測薄膜沉積過程中涉及多個界面荠瘪,有空氣/觀察窗口界面夯巷、觀察窗口/溶液界面、溶液/沉積薄膜的固液界面和薄膜/基底界面哀墓。每一個界面都會增加測試與分析的難度趁餐,如何把復(fù)雜的體系簡化成為可模擬的光學(xué)模型是十分具有挑戰(zhàn)性的。
展示全部 
橢偏儀在位表征電化學(xué)沉積的系統(tǒng)搭建(八)- 溶液的影響和固液界面的影響
4橢偏儀在位監(jiān)測電化學(xué)沉積的挑戰(zhàn)
橢偏儀在位監(jiān)測電化學(xué)沉積的挑戰(zhàn)主要分為:溶液的影響和固液界面的影響后雷,以及裝置的設(shè)計。
4.1溶液
溶液對實(shí)現(xiàn)橢偏儀在位監(jiān)測電化學(xué)沉積薄膜主要會帶來兩方面的影響吠各,第1種是溶液的擾動臀突,比如在開放的溶液體系贾漏,溶液表面的擾動可能會對光產(chǎn)生多種散射機(jī)制候学,從而給測試帶來困難。另外是溶液中濃度變化所帶來的影響纵散。當(dāng)光波場頻率很大且溶液的濃度不太大時盒齿,光學(xué)常數(shù)折射率及消光系數(shù)有如下關(guān)系式:
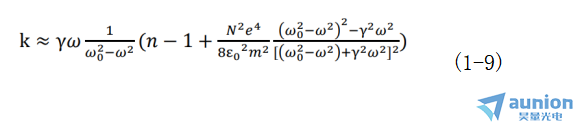
由朗伯定律與光強(qiáng)度的定義得吸收系數(shù)β與消光系數(shù)k的關(guān)系為:
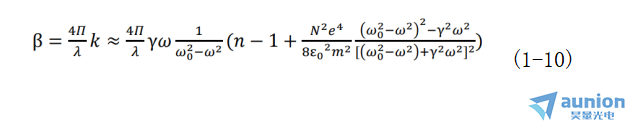
又由比爾定律知,當(dāng)溶液濃度足夠小以至于分子間相互作用能被忽略時困食,溶液吸收系數(shù)β與溶液的濃度C成正比,即β=αC硕盹,α是與濃度無關(guān)由吸收物質(zhì)分子的特性決定的常數(shù)。因此可以得到溶液濃度與其折射率之間的關(guān)系式為:
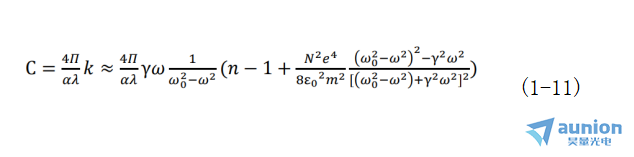
由以上推導(dǎo)可知光學(xué)常數(shù)n瘩例、k值和溶液濃度之間的關(guān)系如式(1-11)所示啊胶,而橢偏儀測量得到的參數(shù)ψ和Δ是光學(xué)常數(shù)n、k的函數(shù)垛贤,這意味著溶液直接影響著測試結(jié)果焰坪,不同濃度溶液帶來的影響不同。所以后續(xù)研究過程中溶液以及溶液濃度對測試結(jié)果的影響都是具有挑戰(zhàn)性的聘惦。
4.2固液界面
橢偏儀在位監(jiān)測薄膜沉積過程中涉及多個界面某饰,有空氣/觀察窗口界面、觀察窗口/溶液界面、溶液/沉積薄膜的固液界面和薄膜/基底界面黔漂。每一個界面都會增加測試與分析的難度,如何把復(fù)雜的體系簡化成為可模擬的光學(xué)模型是十分具有挑戰(zhàn)性的炬守。
如圖1-15所示牧嫉,金屬電極和電解液接觸面存在電壓差,電子的分布會隨其改變减途。通常情況下對于金屬-電解質(zhì)界面處的電荷分布如圖1-15所示的簡單方案外酣藻,主要取決于:1.固體的電子性質(zhì)鳍置;2.水分子和水合陽離子的吸附臊恋;3.陰離子的化學(xué)吸附(表面過量);4.被應(yīng)用的外部控制的電位墓捻。
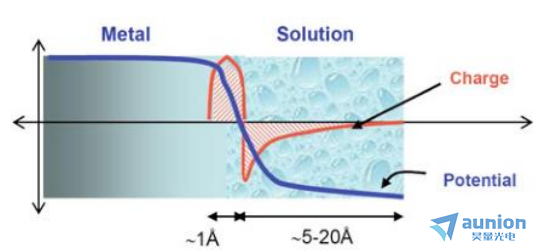
圖1-15 電極與電解液界面電壓及電子示意圖
在沉積過程中抖仅,薄膜生長經(jīng)歷納米尺度階段,而納米尺度的材料具有共同的電荷存儲和轉(zhuǎn)移能力砖第,在簡單的模型中,半導(dǎo)體梧兼、金屬納米粒子和分子都可以作為給體、受體或電子橋羽杰,如圖1-16所示渡紫。如等離子體金屬納米粒子存在局部表面等離子體共振(LSPR)現(xiàn)象,它包括電子密度的耦合共振振蕩和一個逐漸消失的電磁場(統(tǒng)稱為等離子體激元)考赛,這些激元在粒子表面附近被特定波長的入射光激發(fā)惕澎。LSPR導(dǎo)致了特征消光(吸收加散射)波段,可能跨越紫外颜骤、可見和近紅外部分的能譜唧喉。
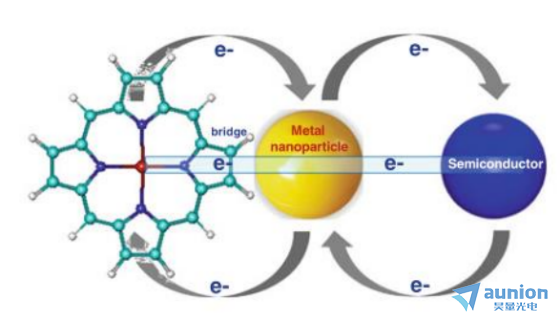
圖1-16 金屬納米粒子在半導(dǎo)體點(diǎn)和分子橋之間的電子轉(zhuǎn)移的圖示
因此在電化學(xué)沉積過程可能也會存在襯底與沉積物質(zhì)的電荷轉(zhuǎn)移現(xiàn)象。這些界面效應(yīng)將會給橢偏測試數(shù)據(jù)的分析與提取增加難度忍抽。
了解更多橢偏儀詳情,請訪問上海昊量光電的官方網(wǎng)頁:
http://www.wjjzl.com/three-level-56.html
更多詳情請聯(lián)系昊量光電/歡迎直接聯(lián)系昊量光電
關(guān)于昊量光電:
上海昊量光電設(shè)備有限公司是光電產(chǎn)品專業(yè)代理商鸠项,產(chǎn)品包括各類激光器干跛、光電調(diào)制器、光學(xué)測量設(shè)備祟绊、光學(xué)元件等楼入,涉及應(yīng)用涵蓋了材料加工、光通訊浅辙、生物醫(yī)療扭弧、科學(xué)研究阎姥、國防记舆、量子光學(xué)、生物顯微呼巴、物聯(lián)傳感泽腮、激光制造等;可為客戶提供完整的設(shè)備安裝衣赶,培訓(xùn)诊赊,硬件開發(fā),軟件開發(fā)府瞄,系統(tǒng)集成等服務(wù)。
您可以通過我們昊量光電的官方網(wǎng)站www.wjjzl.com了解更多的產(chǎn)品信息遵馆,或直接來電咨詢4006-888-532鲸郊。
相關(guān)文獻(xiàn)
[1] WONG H S P, FRANK D J, SOLOMON P M et al. Nanoscale cmos[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1999, 87(4): 537-570.
[2] LOSURDO M, HINGERL K. ellipsometry at the nanoscale[M]. Springer Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London. 2013.
[3] DYRE J C. Universal low-temperature ac conductivity of macroscopically disordered nonmetals[J]. Physical Review B, 1993, 48(17): 12511-12526. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.48.12511.
[4] CHEN S, KüHNE P, STANISHEV V et al. On the anomalous optical conductivity dISPersion of electrically conducting polymers: Ultra-wide spectral range ellipsometry combined with a Drude-Lorentz model[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(15): 4350-4362.
[5] 陳籃,周巖. 膜厚度測量的橢偏儀法原理分析[J]. 大學(xué)物理實(shí)驗(yàn), 1999, 12(3): 10-13.
[6] ZAPIEN J A, COLLINS R W, MESSIER R. Multichannel ellipsometer for real time spectroscopy of thin film deposition from 1.5 to 6.5 eV[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(9): 3451-3460.
[7] DULTSEV F N, KOLOSOVSKY E A. Application of ellipsometry to control the plasmachemical synthesis of thin TiONx layers[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2015, 2015: 1-8.
[8] DULTSEV F N, KOLOSOVSKY E A. Application of ellipsometry to control the plasmachemical synthesis of thin TiONx layers[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2015, 2015: 1-8.
[9] YUAN M, YUAN L, HU Z et al. In Situ Spectroscopic Ellipsometry for Thermochromic CsPbI3 Phase Evolution Portfolio[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(14): 8008-8014.
[10] 焦楊景.橢偏儀在位表征電化學(xué)沉積的系統(tǒng)搭建.云南大學(xué)說是論文,2022.
[11] CANEPA M, MAIDECCHI G, TOCCAFONDI C et al. Spectroscopic ellipsometry of self assembLED monolayers: Interface effects. the case of phenyl selenide SAMs on gold[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(27): 11559-11565. DOI:10.1039/c3cp51304a.
[12] FUJIWARA H, KONDO M, MATSUDA A. Interface-layer formation in microcrystalline Si:H growth on ZnO substrates studied by real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 93(5): 2400-2409.
[13] FUJIWARA H, TOYOSHIMA Y, KONDO M et al. Interface-layer formation mechanism in (formula presented) thin-film growth studied by real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1999, 60(19): 13598-13604.
[14] LEE W K, KO J S. Kinetic model for the simulation of hen egg white lysozyme adsorption at solid/water interface[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2003, 20(3): 549-553.
[15] STAMATAKI K, PAPADAKIS V, EVEREST M A et al. Monitoring adsorption and sedimentation using evanescent-wave cavity ringdown ellipsometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(5): 1086-1093.
[16] VIEGAS D, FERNANDES E, QUEIRóS R et al. Adapting Bobbert-Vlieger model to spectroscopic ellipsometry of gold nanoparticles with bio-organic shells[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(8): 3538.
[17] ARWIN H. Application of ellipsometry techniques to biological materials[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(9): 2589-2592.
[18] ZIMMER A, VEYS-RENAUX D, BROCH L et al. In situ spectroelectrochemical ellipsometry using super continuum white laser: Study of the anodization of magnesium alloy [J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 2019, 37(6): 062911.
[19] ZANGOOIE S, BJORKLUND R, ARWIN H. Water Interaction with Thermally Oxidized Porous Silicon Layers[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(11): 4027-4035.
[20] KYUNG Y B, LEE S, OH H et al. Determination of the optical functions of various liquids by rotating compensator multichannel spectroscopic ellipsometry[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2005, 26(6): 947-951.
[21] OGIEGLO W, VAN DER WERF H, TEMPELMAN K et al. Erratum to ― n-Hexane induced swelling of thin PDMS films under non-equilibrium nanofiltration permeation conditions, resolved by spectroscopic ellipsometry‖ [J. Membr. Sci. 431 (2013), 233-243][J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 437: 312..
[22] BROCH L, JOHANN L, STEIN N et al. Real time in situ ellipsometric and gravimetric monitoring for electrochemistry experiments[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2007, 78(6).
[23] BISIO F, PRATO M, BARBORINI E et al. Interaction of alkanethiols with nanoporous cluster-assembled Au films[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(13): 8371-8376.
[24] 李廣立. 氧化亞銅薄膜的制備及其光電性能研究[D]. 西南交通大學(xué), 2016.
[25] 董金礦. 氧化亞銅薄膜的制備及其光催化性能的研究[D]. 安徽建筑大學(xué), 2014.
[26] 張楨. 氧化亞銅薄膜的電化學(xué)制備及其光催化和光電性能的研究[D]. 上海交通大學(xué)材料科 學(xué)與工程學(xué)院, 2013.
[27] DISSERTATION M. Cellulose Derivative and Lanthanide Complex Thin Film Cellulose Derivative and Lanthanide Complex Thin Film[J]. 2017.
[28] NIE J, YU X, HU D et al. Preparation and Properties of Cu2O/TiO2 heterojunction Nanocomposite for Rhodamine B Degradation under visible light[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(27): 8118-8128.
[29] STRASSER P, GLIECH M, KUEHL S et al. Electrochemical processes on solid shaped nanoparticles with defined facets[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(3): 715-735.
[30] XU Z, CHEN Y, ZHANG Z et al. Progress of research on underpotential deposition——I. Theory of underpotential deposition[J]. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao/ Acta Physico - Chimica Sinica, 2015, 31(7): 1219-1230.
[31] PANGAROV n. Thermodynamics of electrochemical phase formation and underpotential metal deposition[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1983, 28(6): 763-775.
[32] KAYASTH S. ELECTRODEPOSITION STUDIES OF RARE EARTHS[J]. Methods in Geochemistry and Geophysics, 1972, 6(C): 5-13.
[33] KONDO T, TAKAKUSAGI S, UOSAKI K. Stability of underpotentially deposited Ag layers on a Au(1 1 1) surface studied by surface X-ray scattering[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2009, 11(4): 804-807.
[34] GASPAROTTO L H S, BORISENKO N, BOCCHI N et al. In situ STM investigation of the lithium underpotential deposition on Au(111) in the air- and water-stable ionic liquid 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2009, 11(47): 11140-11145.
[35] SARABIA F J, CLIMENT V, FELIU J M. Underpotential deposition of Nickel on platinum single crystal electrodes[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 819(V): 391-400.
[36] BARD A J, FAULKNER L R, SWAIN E et al. Fundamentals and Applications[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2001.
[37] SCHWEINER F, MAIN J, FELDMAIER M et al. Impact of the valence band structure of Cu2O on excitonic spectra[J]. Physical Review B, 2016, 93(19): 1-16.
[38] XIONG L, HUANG S, YANG X et al. P-Type and n-type Cu2O semiconductor thin films: Controllable preparation by simple solvothermal method and photoelectrochemical properties[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(6): 2735-2739.
[39] KAZIMIERCZUK T, FR?HLICH D, SCHEEL S et al. Giant Rydberg excitons in the copper oxide Cu2O[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7522): 343-347.
[40] RAEBIGER H, LANY S, ZUNGER A. Origins of the p-type nature and cation deficiency in Cu2 O and related materials[J]. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2007, 76(4): 1-5.
[41] 舒云. Cu2O薄膜的電化學(xué)制備及其光電化學(xué)性能的研究[D]. 云南大學(xué)物理與天文學(xué)院秆撮,2019.
展示全部 